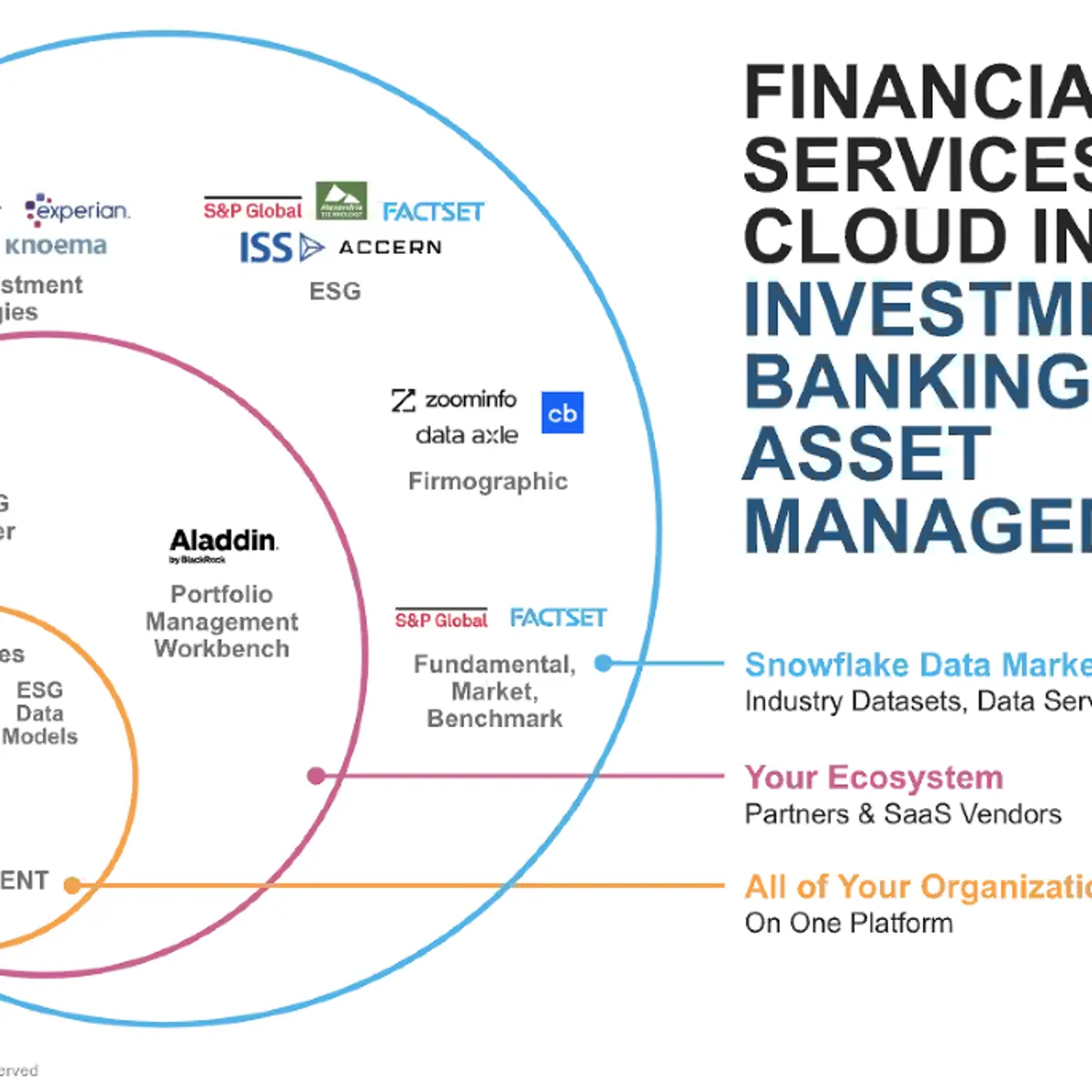
Financial services firms account for a significant portion of Snowflake’s Data Cloud, which is uniquely suited to the industry’s needs.
Indeed, for years many of the world’s leading financial institutions have turned to Snowflake for help creating 360-degree views of their customers, streamlining risk management processes, improving their threat detection, minimizing reputational and financial risk from fraud, and adhering to regulatory guidelines.
The need for a unified, secure, cloud-based platform that can handle vast amounts of data continually increases as developers put more AI applications into production and bring more AI/ML work into Snowflake. Fortunately, Snowflake was built to address this need. It allows firms to scale multiple workloads across their entire data stack using a single copy of
their data, enabling a single source of truth without requiring the organizations to extract, transfer and load information from an existing data warehouse or data lake. And Snowflake Marketplace provides access to over 600 providers and 2,416 live, ready-touse data sets, services and Snowflake Native Apps (as of January 31, 2024).
Meanwhile, regulatory demands and business resilience needs require financial firms to spread their data across multiple clouds. Since Snowflake works seamlessly across multiple providers, organizations can easily use separate clouds to collaborate for different purposes. This gives companies faster access to the global financial services ecosystem of payment processors and application providers. A multicloud
approach is also advantageous when it comes to building business resiliency and better disaster recovery. And because financial services companies can share data entirely within Snowflake, they can exchange data more quickly and cost effectively. Since security and governance are key priorities for financial services firms, strict controls are required in these areas. Snowflake eliminates data replication by
allowing data sharing entirely within the platform, so it’s more secure than legacy data-sharing methods such as FTP, SFTP or email.